The Penn State Stroke Center provides several lifesaving services for stroke, vascular formations, brain disorders and brain aneurysms.
Clot Retrieval – Solitaire Device
The Solitaire FR Device is one of the newest tools to be approved for the treatment of ischemic stroke. Ischemic strokes are the most common type of stroke and are caused by a brain artery becoming blocked, preventing normal blood flow from going to the nearby brain. The Solitaire is one of a class of devices, called a stent retriever, which are a combination of a stent (mesh-like tube typically used to push open narrowed blood vessels) and a retriever (a grasping device usually used to remove material such as blood clots). This combination of properties makes the Solitaire extremely effective in opening up brain arteries that are blocked by a clot during a stroke.
If a patient is found to have an ischemic stroke with a blockage of a large blood vessel that may be opened by the Solitaire, the patient is taken urgently to Penn State Health Milton S. Hershey Medical Center's state-of-the-art neuroendovascular suite. There, a catheter is first placed into the femoral artery in the groin and directed up into the artery in the neck that leads to the blocked brain artery. A smaller catheter (microcatheter) is then fed up to and through the blockage. The Solitaire is delivered through this microcatheter and is opened in the area of the clot. The clot is disrupted or can be pulled out by the device.
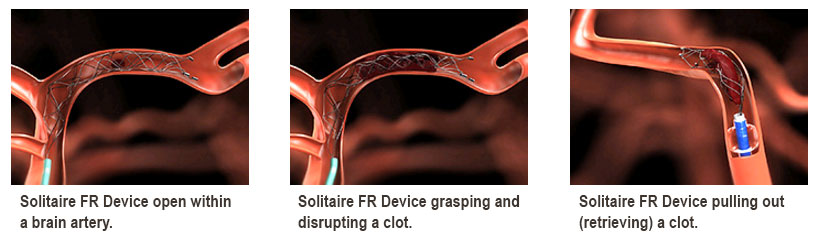
Hershey Medical Center neuroendovascular surgeons were the first physicians in central Pennsylvania to use the Solitaire. Unfortunately, the Solitaire and other devices are not appropriate for all stroke patients. Penn State Stroke Center uses a multidisciplinary team of stroke neurologists and neuroendovascular surgeons to evaluate each patient individually before making a personalized treatment recommendation.


